Task-Aware Low-Light Enhancement for Robotics [GitHub]
-
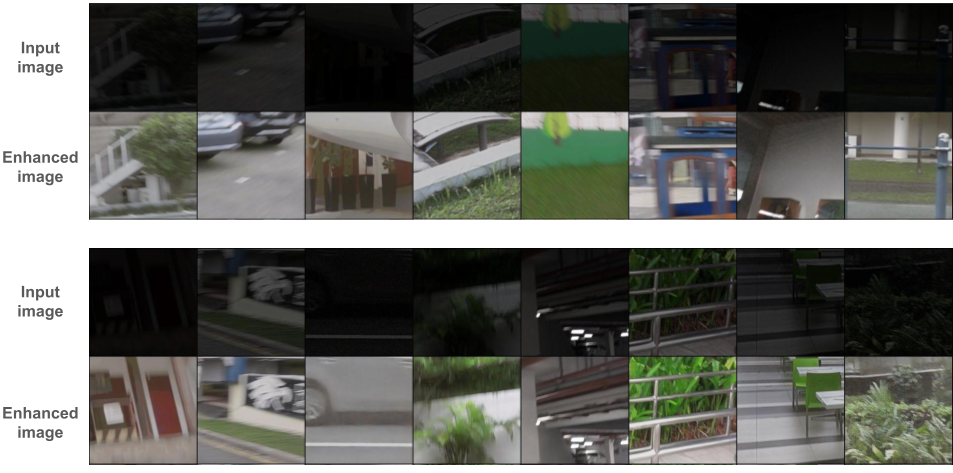 In this project, I developed an algorithm to improve robotic perception under challenging low-light conditions. Traditional image enhancers focus on visual metrics like PSNR or SSIM,
but this work is task-aware — it learns to optimize what matters for robots: feature matching and object detection. The system combines a lightweight CNN architecture with a two-stage training
strategy: (1) paired pretraining on LOL-Blur and LOL-v2 (Real) to learn natural enhancement, and (2) task-aware fine-tuning using ExDark and MID datasets to directly improve LoFTR keypoint matching
and YOLO detection performance. Trained efficiently on Colab with mixed precision (AMP), this work achieves tangible downstream gains — increasing LoFTR inliers by over 80% and improving YOLO mAP@0.5
from 0.582 → 0.644 after adaptation. The project demonstrates how perceptual enhancement can be re-framed as a robotics performance optimization problem, bridging low-level image quality with
high-level visual understanding.
In this project, I developed an algorithm to improve robotic perception under challenging low-light conditions. Traditional image enhancers focus on visual metrics like PSNR or SSIM,
but this work is task-aware — it learns to optimize what matters for robots: feature matching and object detection. The system combines a lightweight CNN architecture with a two-stage training
strategy: (1) paired pretraining on LOL-Blur and LOL-v2 (Real) to learn natural enhancement, and (2) task-aware fine-tuning using ExDark and MID datasets to directly improve LoFTR keypoint matching
and YOLO detection performance. Trained efficiently on Colab with mixed precision (AMP), this work achieves tangible downstream gains — increasing LoFTR inliers by over 80% and improving YOLO mAP@0.5
from 0.582 → 0.644 after adaptation. The project demonstrates how perceptual enhancement can be re-framed as a robotics performance optimization problem, bridging low-level image quality with
high-level visual understanding.
HDR Pre-processing for Visual Odometry [GitHub]
-
I developed a lightweight HDR pre-processing stage that converts SDR input to HDR format and converts the HDR back to SDR using a piecewise curve to preserve highlight and shadow detail,
improving the robustness of ORB-SLAM3 under extreme contrast. I also evaluated on EuRoC MAV and TUM RGB-D using APE (Sim3, translation) and RPE (Δ=5 frames). The proposed method achieved consistent
improvements over the baseline. Pooled results across datasets: APE −8.8%, RPE −6.2%; on TUM specifically: APE −10.6% with a 77% win-rate, and RPE −12.3%. Classical baselines
were included for comparison, and all experiments were fully reproducible via Docker/Conda scripts with fixed VO configurations and timestamps.
Learned Pre-Processing for Perceptual Quality Optimization [GitHub]
-
In this project, I developed a deep learning system that optimizes input data before processing to significantly improve perceptual quality metrics. The approach uses a U-Net architecture with a
Detail Compensation Module (DCM) trained end-to-end using differentiable proxy models—a quality metric estimator and a processing pipeline simulator—enabling gradient-based optimization of
traditionally non-differentiable systems. This methodology allows neural networks to learn optimal input transformations by backpropagating through proxy representations of complex processing chains,
opening applications in compression, transmission, enhancement, and other quality-sensitive pipelines. Evaluation on 183,660 test samples shows a mean improvement of 21.2 VMAF quality points.
The model achieves a 99.99% success rate with only 0.01% degradation cases, validating the proxy-based training methodology. These results translate to practical efficiency gains of 30-40% at equivalent perceptual
quality. The framework is pipeline-agnostic and can be adapted to various domains including video compression, image transmission, medical imaging preprocessing, and neural network input optimization,
demonstrating the broad applicability of differentiable proxy-based learning for optimizing non-differentiable systems.
Deep learning based encoder proxy [GitHub]
-
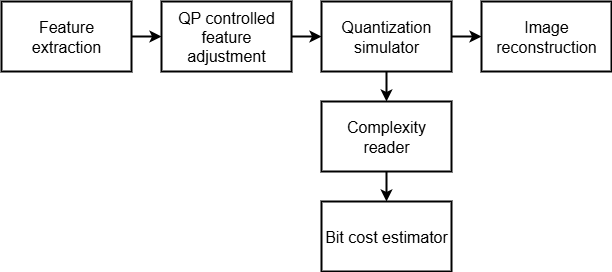 This work is one piece of a larger research effort to improve the VMAF score between the input and output of a video encoder by means of
deep learning based pre-processing algorithms. Here, I created a neural encoder-decoder that simulates video encoder behavior by generating reconstructed frames matching actual encoder output,
achieving 30.73 dB PSNR and 0.931 MS-SSIM across 140K test samples. The architecture combines GDN normalization, FiLM conditioning for CRF-based quality control, and learned quantization to capture
compression artifacts without running full encoder pipelines. The model successfully learned encoder behavior patterns, showing systematic quality degradation from CRF 19-51 that mirrors actual encoder characteristics.
While the 4-9 dB PSNR gap from real encoders limits direct replacement applications, the 10-100x speed advantage enables rapid compression research, streaming optimization prototyping, and educational
demonstrations of encoder behavior.
This work is one piece of a larger research effort to improve the VMAF score between the input and output of a video encoder by means of
deep learning based pre-processing algorithms. Here, I created a neural encoder-decoder that simulates video encoder behavior by generating reconstructed frames matching actual encoder output,
achieving 30.73 dB PSNR and 0.931 MS-SSIM across 140K test samples. The architecture combines GDN normalization, FiLM conditioning for CRF-based quality control, and learned quantization to capture
compression artifacts without running full encoder pipelines. The model successfully learned encoder behavior patterns, showing systematic quality degradation from CRF 19-51 that mirrors actual encoder characteristics.
While the 4-9 dB PSNR gap from real encoders limits direct replacement applications, the 10-100x speed advantage enables rapid compression research, streaming optimization prototyping, and educational
demonstrations of encoder behavior.
Deep-Learning based VMAF proxy [GitHub]
-
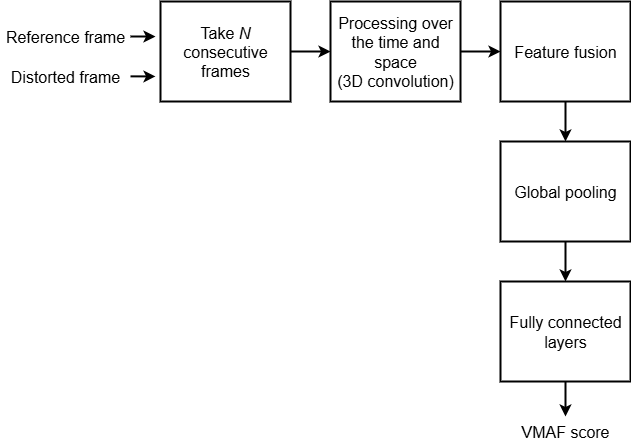 In this work, I developed a lightweight 3D CNN that predicts VMAF video quality scores from reference and distorted frame sequences, achieving strong correlation (PLCC 0.915) with ground truth on
183K test samples. The Siamese architecture processes temporal frame triplets through specialized 3D convolutions, achieving particularly impressive accuracy on high-quality content
(MAE 3.58 for 85-100 VMAF range) while maintaining only 2.1M parameters for real-time deployment. I built this project on Google Vertex AI with advanced training strategies, gradient clipping, and
learning rate scheduling to overcome gradient instability issues. The model demonstrates production-ready performance for content ranking and quality monitoring applications, though absolute accuracy
limitations (overall MAE 7.04) make it better suited for relative quality assessment than precise VMAF score prediction.
In this work, I developed a lightweight 3D CNN that predicts VMAF video quality scores from reference and distorted frame sequences, achieving strong correlation (PLCC 0.915) with ground truth on
183K test samples. The Siamese architecture processes temporal frame triplets through specialized 3D convolutions, achieving particularly impressive accuracy on high-quality content
(MAE 3.58 for 85-100 VMAF range) while maintaining only 2.1M parameters for real-time deployment. I built this project on Google Vertex AI with advanced training strategies, gradient clipping, and
learning rate scheduling to overcome gradient instability issues. The model demonstrates production-ready performance for content ranking and quality monitoring applications, though absolute accuracy
limitations (overall MAE 7.04) make it better suited for relative quality assessment than precise VMAF score prediction.
Perception-based Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) to High Dynamic Range (HDR) conversion [Conference Paper][Journal Paper]
-
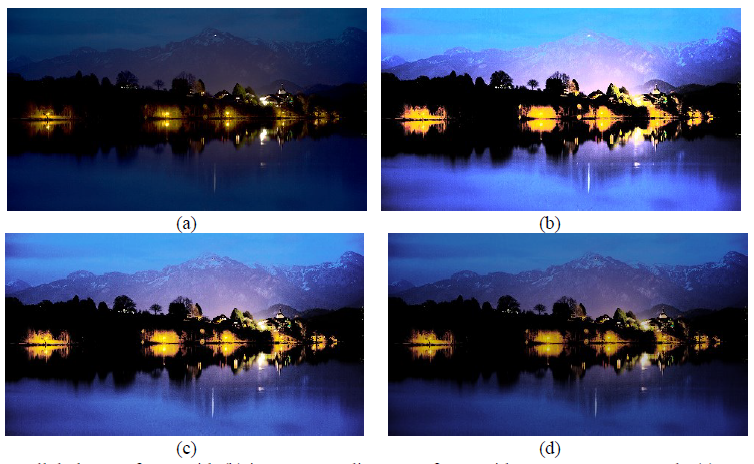 The drastic visual improvements introduced by HDR
technologies open new markets for a wide range of industries. In this project, through modeling
the behavior of the human eye, I propose a novel high visual quality video inverse Tone Mapping Operator (iTMO) that addresses the
inadequacies of the state-of-the-art methods, resulting in high visual quality HDR videos that match the capabilities of the HDR technology.
This algorithm uses a hybrid approach to achieve an optimal balance between the overall contrast and brightness of the output HDR frame
by maximizing a weighted sum of contrast and brightness difference between input SDR and generated HDR frame.
Our subjective evaluations demonstrated that the proposed algorithm outperforms the existing methods by an average of 75% in terms of
visual quality. Further testing using HDR VDP and
PU-SSIM objective quality metrics demonstrated that our
algorithm outperforms existing methods on a wide variety of input content.
The drastic visual improvements introduced by HDR
technologies open new markets for a wide range of industries. In this project, through modeling
the behavior of the human eye, I propose a novel high visual quality video inverse Tone Mapping Operator (iTMO) that addresses the
inadequacies of the state-of-the-art methods, resulting in high visual quality HDR videos that match the capabilities of the HDR technology.
This algorithm uses a hybrid approach to achieve an optimal balance between the overall contrast and brightness of the output HDR frame
by maximizing a weighted sum of contrast and brightness difference between input SDR and generated HDR frame.
Our subjective evaluations demonstrated that the proposed algorithm outperforms the existing methods by an average of 75% in terms of
visual quality. Further testing using HDR VDP and
PU-SSIM objective quality metrics demonstrated that our
algorithm outperforms existing methods on a wide variety of input content.
Frame-level rate Control for real-time video applications
-
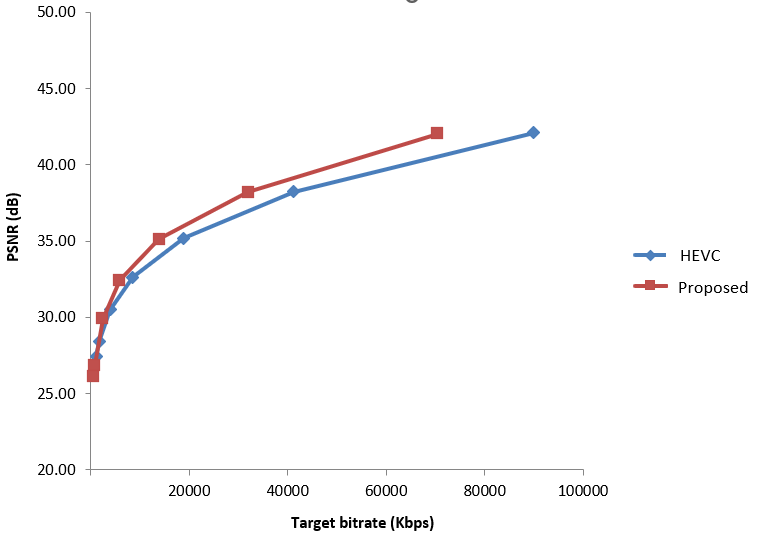 Rate control module is a critical component of a video encoder, especially for low-delay applications such as cloud gaming,
live streaming, and video conferencing. It ensures that video data is transmitted efficiently and smoothly, maintaining high visual
quality while adapting to varying network conditions and content complexity. In this work, I developed a frame-level
video rate control algorithm for NETINT Technologies's next-generation
Video Processing Units (VPUs). Our algorithm is content adaptive, delivering outstanding performance improvements in terms of BD-rate.
These enhancements are codec-agnostic, demonstrating consistent gains across AVC, HEVC, and AV1 codecs. Our algorithm achieves an
average of 10% improvement in BD-rate compared to previous generation encoders, reflecting its efficiency in maintaining high visual
quality at reduced bitrates.
Rate control module is a critical component of a video encoder, especially for low-delay applications such as cloud gaming,
live streaming, and video conferencing. It ensures that video data is transmitted efficiently and smoothly, maintaining high visual
quality while adapting to varying network conditions and content complexity. In this work, I developed a frame-level
video rate control algorithm for NETINT Technologies's next-generation
Video Processing Units (VPUs). Our algorithm is content adaptive, delivering outstanding performance improvements in terms of BD-rate.
These enhancements are codec-agnostic, demonstrating consistent gains across AVC, HEVC, and AV1 codecs. Our algorithm achieves an
average of 10% improvement in BD-rate compared to previous generation encoders, reflecting its efficiency in maintaining high visual
quality at reduced bitrates.
Enhancing video temporal consistency [Journal Paper]
-
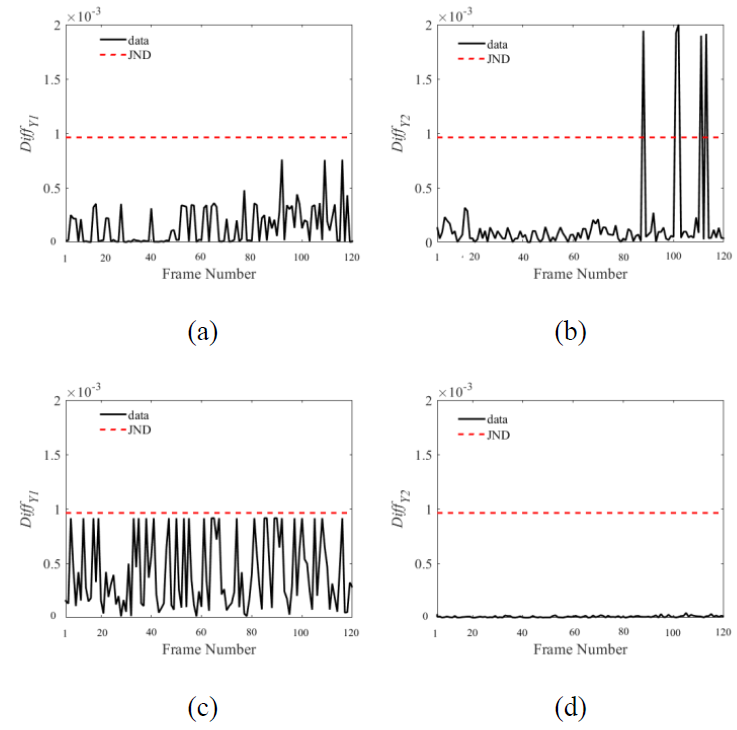 Maintaining consistent luminance is crucial for delivering high-quality viewing experiences.
Unwanted fluctuations in brightness, often perceived as flickering, can detract from the visual appeal and clarity of images
and videos. In this work, I address this challenge by implementing a condition on any brightness conversion that limits brightness
fluctuations to less than one Just Noticeable Difference (JND), effectively preventing perceptible flickering.
By ensuring that changes in brightness remain below the human threshold of detection, our algorithm guarantees a stable and
consistent luminance output, enhancing the viewer's experience.
Maintaining consistent luminance is crucial for delivering high-quality viewing experiences.
Unwanted fluctuations in brightness, often perceived as flickering, can detract from the visual appeal and clarity of images
and videos. In this work, I address this challenge by implementing a condition on any brightness conversion that limits brightness
fluctuations to less than one Just Noticeable Difference (JND), effectively preventing perceptible flickering.
By ensuring that changes in brightness remain below the human threshold of detection, our algorithm guarantees a stable and
consistent luminance output, enhancing the viewer's experience.
Fully automatic, content adaptive SDR to HDR conversion [Journal Paper][Patent]
-
 Converting SDR content to HDR format to take advantage of the superior visual quality offered by HDR displays,
is an attractive proposition to SDR content owners and real-time broadcasters. In this work, I proposed a novel content
adaptive algorithm that models the sensitivity of the human eye to brightness changes in different
areas of a scene. By processing each frame indepently, our algorithms assigns different weights to different regions of a scene
depending on their pixel distribution. Our subjective evaluations indicate that our proposed method outperforms other
state-of-the-art methods by an average of 80% in terms of visual quality. In addition to subjective evaluations,
I also performed objective evaluations using HDR-VDP and PU-SSIM metrics and concluded that, on average,
our proposed iTMO outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of these two metrics.
Converting SDR content to HDR format to take advantage of the superior visual quality offered by HDR displays,
is an attractive proposition to SDR content owners and real-time broadcasters. In this work, I proposed a novel content
adaptive algorithm that models the sensitivity of the human eye to brightness changes in different
areas of a scene. By processing each frame indepently, our algorithms assigns different weights to different regions of a scene
depending on their pixel distribution. Our subjective evaluations indicate that our proposed method outperforms other
state-of-the-art methods by an average of 80% in terms of visual quality. In addition to subjective evaluations,
I also performed objective evaluations using HDR-VDP and PU-SSIM metrics and concluded that, on average,
our proposed iTMO outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of these two metrics.
Block-Level Rate Control for Enhanced Video Encoding
-
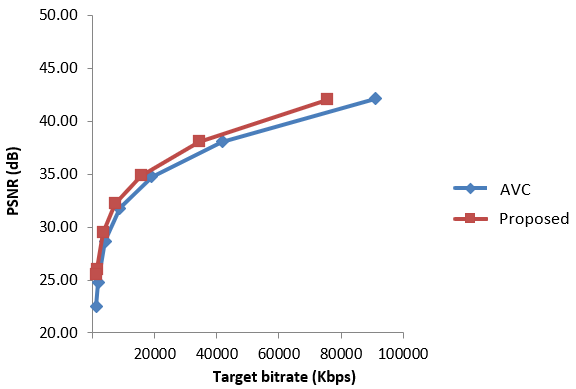 Block-level rate control, particularly at the Coding Tree Unit (CTU) level, is a crucial aspect of video encoding that focuses on
optimizing bitrate allocation within individual blocks of a video frame. This fine-grained approach allows for more precise control
over video quality and compression efficiency. In this project, by analyzing the complexity of each block, I developed a block-level
rate control algorithm for NETINT Technologies's next-generation VPUs. This algorithm
delivers substantial improvements in video encoding performance, achieving an average BD-rate gain of 12% over previous generation
encoders. These enhancements provide consistent benefits across AVC, HEVC, and AV1 codecs.
Block-level rate control, particularly at the Coding Tree Unit (CTU) level, is a crucial aspect of video encoding that focuses on
optimizing bitrate allocation within individual blocks of a video frame. This fine-grained approach allows for more precise control
over video quality and compression efficiency. In this project, by analyzing the complexity of each block, I developed a block-level
rate control algorithm for NETINT Technologies's next-generation VPUs. This algorithm
delivers substantial improvements in video encoding performance, achieving an average BD-rate gain of 12% over previous generation
encoders. These enhancements provide consistent benefits across AVC, HEVC, and AV1 codecs.
-
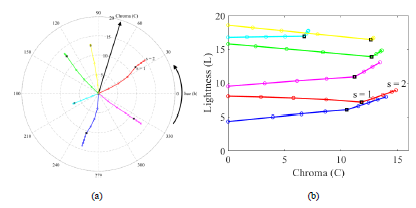 Color adjustment plays a pivotal role in image processing and visual media, ensuring that the representation of colors remains true
to their intended appearance despite variations in lighting and display conditions. As brightness levels change, the hue and saturation
of colors can be unintentionally altered, leading to discrepancies that affect the visual quality and accuracy of images.
In this project, I developed a novel color adjustment algorithm designed to effectively manage changes in hue as brightness levels
are altered. The algorithm's effectiveness is demonstrated through a series of analyses comparing it to existing
methods. Our subjective results indicate that our proposed algorithm outperforms the existing methods by 70% in terms of how closely the
output colors match their input counterparts.
Color adjustment plays a pivotal role in image processing and visual media, ensuring that the representation of colors remains true
to their intended appearance despite variations in lighting and display conditions. As brightness levels change, the hue and saturation
of colors can be unintentionally altered, leading to discrepancies that affect the visual quality and accuracy of images.
In this project, I developed a novel color adjustment algorithm designed to effectively manage changes in hue as brightness levels
are altered. The algorithm's effectiveness is demonstrated through a series of analyses comparing it to existing
methods. Our subjective results indicate that our proposed algorithm outperforms the existing methods by 70% in terms of how closely the
output colors match their input counterparts.
Constant Rate Factor (CRF) algorithm for Enhanced Video Encoding
-
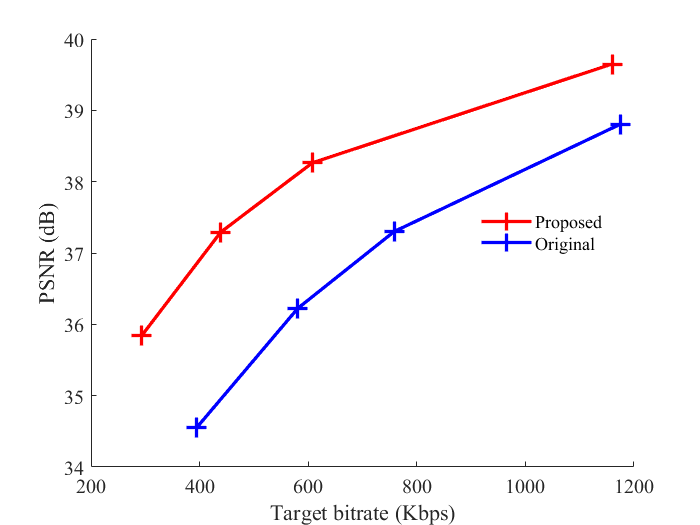 In video processing, achieving high visual quality while keeping file sizes manageable is a
constant challenge. The Constant Rate Factor (CRF) rate control algorithm plays a vital role here, acting as a smart mechanism to
balance quality and compression efficiency. This makes it essential for applications like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing,
where both clarity and bandwidth matter. At NETINT Technologies, I developed an optimized
CRF rate control algorithms for hardware-based VPUs. I developed two variants—uncapped and capped CRF—improving compression efficiency
by 5-10% (BD-rate gains) compared to the original IP. My work, integrated into NETINT’s products, elevated performance and strengthened the
company’s leadership in video processing technology.
In video processing, achieving high visual quality while keeping file sizes manageable is a
constant challenge. The Constant Rate Factor (CRF) rate control algorithm plays a vital role here, acting as a smart mechanism to
balance quality and compression efficiency. This makes it essential for applications like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing,
where both clarity and bandwidth matter. At NETINT Technologies, I developed an optimized
CRF rate control algorithms for hardware-based VPUs. I developed two variants—uncapped and capped CRF—improving compression efficiency
by 5-10% (BD-rate gains) compared to the original IP. My work, integrated into NETINT’s products, elevated performance and strengthened the
company’s leadership in video processing technology.
2-Pass video rate control for latency-tolerant applications
-
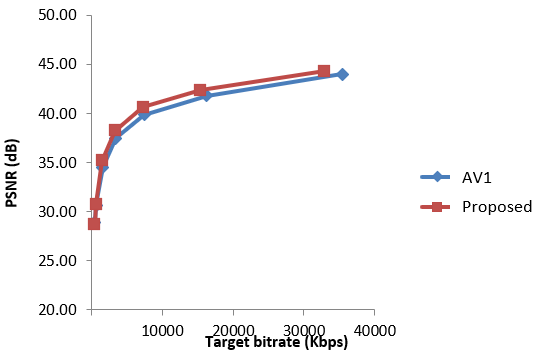 2-pass video rate control is a strategic approach used in latency-tolerant applications, such as Video on Demand (VoD),
where the emphasis is on achieving optimal video quality and precise bitrate management. Unlike single-pass methods, 2-pass
rate control analyzes the video content in two stages, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of both current and future
frame complexities. In this project, implemented in NETINT Technologies's next-generation VPUs,
I developed a 2-pass video rate control algorithm designed to enhance both BD-rate performance and target bitrate tracking for
VoD applications. By analyzing the complexity of current and future frames, the algorithm efficiently assigns Quantization
Parameters (QPs) to each frame. This results in an average BD-rate improvement of 6% compared to previous generation algorithms,
along with a 3% enhancement in target tracking accuracy. These improvements are consistently observed across various codecs,
including AVC, HEVC, and AV1.
2-pass video rate control is a strategic approach used in latency-tolerant applications, such as Video on Demand (VoD),
where the emphasis is on achieving optimal video quality and precise bitrate management. Unlike single-pass methods, 2-pass
rate control analyzes the video content in two stages, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of both current and future
frame complexities. In this project, implemented in NETINT Technologies's next-generation VPUs,
I developed a 2-pass video rate control algorithm designed to enhance both BD-rate performance and target bitrate tracking for
VoD applications. By analyzing the complexity of current and future frames, the algorithm efficiently assigns Quantization
Parameters (QPs) to each frame. This results in an average BD-rate improvement of 6% compared to previous generation algorithms,
along with a 3% enhancement in target tracking accuracy. These improvements are consistently observed across various codecs,
including AVC, HEVC, and AV1.
-
 In this project, I developed an image segmentation algorithm based in the theory of entropy.
The primary objective was to effectively categorize an image into three distinct brightness regions: dark, normal, and bright.
By leveraging entropy, a measure of undertainty, the algorithm intelligently identifies the most informative thresholds to segment the
image. The segmented results is an image where each region is clearly defined, facilitating further analysis or processing tasks.
This method proves particularly useful in applications such as medical imaging, remote sensing, and computer vision, where precise
segmentation can lead to more accurate interpretations and decisions.
In this project, I developed an image segmentation algorithm based in the theory of entropy.
The primary objective was to effectively categorize an image into three distinct brightness regions: dark, normal, and bright.
By leveraging entropy, a measure of undertainty, the algorithm intelligently identifies the most informative thresholds to segment the
image. The segmented results is an image where each region is clearly defined, facilitating further analysis or processing tasks.
This method proves particularly useful in applications such as medical imaging, remote sensing, and computer vision, where precise
segmentation can lead to more accurate interpretations and decisions.
Enhancing AV1 Compression with Extended Directional Intra Modes
-
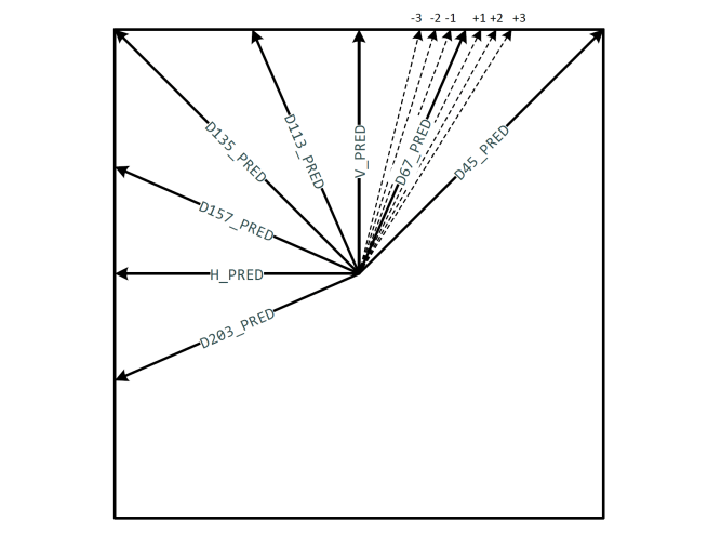 The AV1 codec, an open-source video compression standard, excels in intra-frame prediction, where directional
intra modes predict pixel values using neighboring pixels to optimize file sizes. My work at NETINT Technologies
focused on extending these modes to boost AV1’s efficiency. Through this enhancement, I improved the BD-rate performance by an average of
2% across all intra cases. This translates to better compression—offering either higher video quality at the same bitrate or equivalent
quality at a lower bitrate. For industries like video streaming and storage, this means reduced bandwidth demands and improved user experiences.
Integrated into NETINT’s video processing solutions, this advancement underscores my ability to refine complex codecs and deliver tangible
performance gains.
The AV1 codec, an open-source video compression standard, excels in intra-frame prediction, where directional
intra modes predict pixel values using neighboring pixels to optimize file sizes. My work at NETINT Technologies
focused on extending these modes to boost AV1’s efficiency. Through this enhancement, I improved the BD-rate performance by an average of
2% across all intra cases. This translates to better compression—offering either higher video quality at the same bitrate or equivalent
quality at a lower bitrate. For industries like video streaming and storage, this means reduced bandwidth demands and improved user experiences.
Integrated into NETINT’s video processing solutions, this advancement underscores my ability to refine complex codecs and deliver tangible
performance gains.
Enhanced target tracking for low-delay rate control algorithms
-
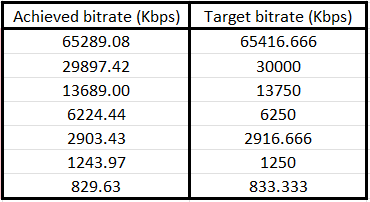 In low-delay applications, such as live streaming and interactive video services, maintaining precise target tracking in rate
control algorithms is essential for delivering consistent video quality and minimizing latency. In this project, I developed an
innovative approach to enhance the target tracking performance of low-delay rate control algorithms. By analyzing the complexity of
different regions within a frame, the algorithm accurately estimates the frame's target size. This detailed analysis allows for more
precise bitrate distribution, resulting in an average improvement of 5% in target tracking performance compared to previous generation
algorithms.
In low-delay applications, such as live streaming and interactive video services, maintaining precise target tracking in rate
control algorithms is essential for delivering consistent video quality and minimizing latency. In this project, I developed an
innovative approach to enhance the target tracking performance of low-delay rate control algorithms. By analyzing the complexity of
different regions within a frame, the algorithm accurately estimates the frame's target size. This detailed analysis allows for more
precise bitrate distribution, resulting in an average improvement of 5% in target tracking performance compared to previous generation
algorithms.
Advanced post-processing for enhanced BD-Rate VMAF in video encoders
-
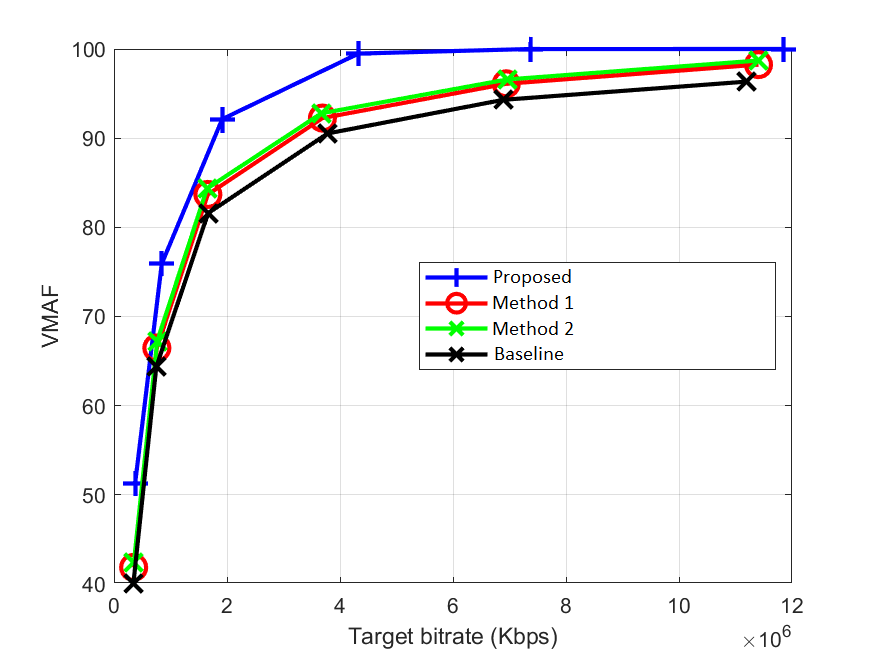 In the realm of video encoding, optimizing the BD-rate VMAF score is critical for achieving superior video quality while maintaining
efficient bitrate usage. Video Multi-Method Assessment Fusion (VMAF) is a
perceptual video quality metric that combines multiple assessment methods to provide a comprehensive evaluation of video quality.
In this project, I developed post-processing techniques focused on the brightness and color channels of input video
sequences. This approach significantly enhanced the BD-rate VMAF score by an average of 24%, demonstrating substantial improvements
in video quality without compromising the original look and artistic impression of the videos. The transformations applied are
meticulously designed to preserve the aesthetic integrity of the content. The gains achieved through this method are consistent across
various rate control modes, including Constant Quantization Parameter (CQP), Constant Bitrate (CBR), and Constant Rate Factor (CRF).
In the realm of video encoding, optimizing the BD-rate VMAF score is critical for achieving superior video quality while maintaining
efficient bitrate usage. Video Multi-Method Assessment Fusion (VMAF) is a
perceptual video quality metric that combines multiple assessment methods to provide a comprehensive evaluation of video quality.
In this project, I developed post-processing techniques focused on the brightness and color channels of input video
sequences. This approach significantly enhanced the BD-rate VMAF score by an average of 24%, demonstrating substantial improvements
in video quality without compromising the original look and artistic impression of the videos. The transformations applied are
meticulously designed to preserve the aesthetic integrity of the content. The gains achieved through this method are consistent across
various rate control modes, including Constant Quantization Parameter (CQP), Constant Bitrate (CBR), and Constant Rate Factor (CRF).
Comprehensive SDR/HDR conversion suite for enhanced video compatibility
-
The seamless conversion between Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) and High Dynamic Range (HDR) formats is essential for ensuring compatibility
and optimal viewing experiences across diverse display technologies. In this project, I developed a SDR/HDR conversion suite for
NETINT Technologies's next generation VPUs, capable of performing three distinct types of
conversions. This suite offers robust solutions for converting SDR input to HDR format, transforming HDR input to SDR format, and
converting between different HDR formats, such as Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG) to
HDR10. Each conversion process is meticulously designed to preserve the
visual integrity and artistic intent of the original content, ensuring that the resulting output meets the highest standards of
quality and compatibility. The hardware implementation of this suite ensures high performance and efficiency, making it
suitable for real-time applications and large-scale deployments.
Comprehensive survey on image and video quality assessment [Journal Paper]
-
In this survey paper, I conducted an extensive review of both subjective and objective methods
for assessing image and video quality. The project aimed to bridge the gap between human perception and algorithmic evaluation,
providing a holistic view of current methodologies and their applications. Subjective assessment involves human observers to
evaluate quality. In contrast, objective assessment leverages computational models to predict quality scores, offering efficiency
and consistency in evaluation. This survey meticulously categorizes and compares various assessment techniques, highlighting their
strengths, limitations, and potential areas for improvement. This work has been cited over 250 times in prestigous journals and conferences.
 In this project, I developed an algorithm to improve robotic perception under challenging low-light conditions. Traditional image enhancers focus on visual metrics like PSNR or SSIM,
but this work is task-aware — it learns to optimize what matters for robots: feature matching and object detection. The system combines a lightweight CNN architecture with a two-stage training
strategy: (1) paired pretraining on LOL-Blur and LOL-v2 (Real) to learn natural enhancement, and (2) task-aware fine-tuning using ExDark and MID datasets to directly improve LoFTR keypoint matching
and YOLO detection performance. Trained efficiently on Colab with mixed precision (AMP), this work achieves tangible downstream gains — increasing LoFTR inliers by over 80% and improving YOLO mAP@0.5
from 0.582 → 0.644 after adaptation. The project demonstrates how perceptual enhancement can be re-framed as a robotics performance optimization problem, bridging low-level image quality with
high-level visual understanding.
In this project, I developed an algorithm to improve robotic perception under challenging low-light conditions. Traditional image enhancers focus on visual metrics like PSNR or SSIM,
but this work is task-aware — it learns to optimize what matters for robots: feature matching and object detection. The system combines a lightweight CNN architecture with a two-stage training
strategy: (1) paired pretraining on LOL-Blur and LOL-v2 (Real) to learn natural enhancement, and (2) task-aware fine-tuning using ExDark and MID datasets to directly improve LoFTR keypoint matching
and YOLO detection performance. Trained efficiently on Colab with mixed precision (AMP), this work achieves tangible downstream gains — increasing LoFTR inliers by over 80% and improving YOLO mAP@0.5
from 0.582 → 0.644 after adaptation. The project demonstrates how perceptual enhancement can be re-framed as a robotics performance optimization problem, bridging low-level image quality with
high-level visual understanding.
 This work is one piece of a larger research effort to improve the
This work is one piece of a larger research effort to improve the  In this work, I developed a lightweight 3D CNN that predicts VMAF video quality scores from reference and distorted frame sequences, achieving strong correlation (PLCC 0.915) with ground truth on
183K test samples. The Siamese architecture processes temporal frame triplets through specialized 3D convolutions, achieving particularly impressive accuracy on high-quality content
(MAE 3.58 for 85-100 VMAF range) while maintaining only 2.1M parameters for real-time deployment. I built this project on Google Vertex AI with advanced training strategies, gradient clipping, and
learning rate scheduling to overcome gradient instability issues. The model demonstrates production-ready performance for content ranking and quality monitoring applications, though absolute accuracy
limitations (overall MAE 7.04) make it better suited for relative quality assessment than precise VMAF score prediction.
In this work, I developed a lightweight 3D CNN that predicts VMAF video quality scores from reference and distorted frame sequences, achieving strong correlation (PLCC 0.915) with ground truth on
183K test samples. The Siamese architecture processes temporal frame triplets through specialized 3D convolutions, achieving particularly impressive accuracy on high-quality content
(MAE 3.58 for 85-100 VMAF range) while maintaining only 2.1M parameters for real-time deployment. I built this project on Google Vertex AI with advanced training strategies, gradient clipping, and
learning rate scheduling to overcome gradient instability issues. The model demonstrates production-ready performance for content ranking and quality monitoring applications, though absolute accuracy
limitations (overall MAE 7.04) make it better suited for relative quality assessment than precise VMAF score prediction.
 The drastic visual improvements introduced by
The drastic visual improvements introduced by  Rate control module is a critical component of a video encoder, especially for low-delay applications such as cloud gaming,
live streaming, and video conferencing. It ensures that video data is transmitted efficiently and smoothly, maintaining high visual
quality while adapting to varying network conditions and content complexity. In this work, I developed a frame-level
video rate control algorithm for
Rate control module is a critical component of a video encoder, especially for low-delay applications such as cloud gaming,
live streaming, and video conferencing. It ensures that video data is transmitted efficiently and smoothly, maintaining high visual
quality while adapting to varying network conditions and content complexity. In this work, I developed a frame-level
video rate control algorithm for  Maintaining consistent luminance is crucial for delivering high-quality viewing experiences.
Unwanted fluctuations in brightness, often perceived as flickering, can detract from the visual appeal and clarity of images
and videos. In this work, I address this challenge by implementing a condition on any brightness conversion that limits brightness
fluctuations to less than one Just Noticeable Difference (JND), effectively preventing perceptible flickering.
By ensuring that changes in brightness remain below the human threshold of detection, our algorithm guarantees a stable and
consistent luminance output, enhancing the viewer's experience.
Maintaining consistent luminance is crucial for delivering high-quality viewing experiences.
Unwanted fluctuations in brightness, often perceived as flickering, can detract from the visual appeal and clarity of images
and videos. In this work, I address this challenge by implementing a condition on any brightness conversion that limits brightness
fluctuations to less than one Just Noticeable Difference (JND), effectively preventing perceptible flickering.
By ensuring that changes in brightness remain below the human threshold of detection, our algorithm guarantees a stable and
consistent luminance output, enhancing the viewer's experience.
 Converting SDR content to HDR format to take advantage of the superior visual quality offered by HDR displays,
is an attractive proposition to SDR content owners and real-time broadcasters. In this work, I proposed a novel content
adaptive algorithm that models the sensitivity of the human eye to brightness changes in different
areas of a scene. By processing each frame indepently, our algorithms assigns different weights to different regions of a scene
depending on their pixel distribution. Our subjective evaluations indicate that our proposed method outperforms other
state-of-the-art methods by an average of 80% in terms of visual quality. In addition to subjective evaluations,
I also performed objective evaluations using HDR-VDP and PU-SSIM metrics and concluded that, on average,
our proposed iTMO outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of these two metrics.
Converting SDR content to HDR format to take advantage of the superior visual quality offered by HDR displays,
is an attractive proposition to SDR content owners and real-time broadcasters. In this work, I proposed a novel content
adaptive algorithm that models the sensitivity of the human eye to brightness changes in different
areas of a scene. By processing each frame indepently, our algorithms assigns different weights to different regions of a scene
depending on their pixel distribution. Our subjective evaluations indicate that our proposed method outperforms other
state-of-the-art methods by an average of 80% in terms of visual quality. In addition to subjective evaluations,
I also performed objective evaluations using HDR-VDP and PU-SSIM metrics and concluded that, on average,
our proposed iTMO outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of these two metrics.
 Block-level rate control, particularly at the Coding Tree Unit (CTU) level, is a crucial aspect of video encoding that focuses on
optimizing bitrate allocation within individual blocks of a video frame. This fine-grained approach allows for more precise control
over video quality and compression efficiency. In this project, by analyzing the complexity of each block, I developed a block-level
rate control algorithm for
Block-level rate control, particularly at the Coding Tree Unit (CTU) level, is a crucial aspect of video encoding that focuses on
optimizing bitrate allocation within individual blocks of a video frame. This fine-grained approach allows for more precise control
over video quality and compression efficiency. In this project, by analyzing the complexity of each block, I developed a block-level
rate control algorithm for  Color adjustment plays a pivotal role in image processing and visual media, ensuring that the representation of colors remains true
to their intended appearance despite variations in lighting and display conditions. As brightness levels change, the hue and saturation
of colors can be unintentionally altered, leading to discrepancies that affect the visual quality and accuracy of images.
In this project, I developed a novel color adjustment algorithm designed to effectively manage changes in hue as brightness levels
are altered. The algorithm's effectiveness is demonstrated through a series of analyses comparing it to existing
methods. Our subjective results indicate that our proposed algorithm outperforms the existing methods by 70% in terms of how closely the
output colors match their input counterparts.
Color adjustment plays a pivotal role in image processing and visual media, ensuring that the representation of colors remains true
to their intended appearance despite variations in lighting and display conditions. As brightness levels change, the hue and saturation
of colors can be unintentionally altered, leading to discrepancies that affect the visual quality and accuracy of images.
In this project, I developed a novel color adjustment algorithm designed to effectively manage changes in hue as brightness levels
are altered. The algorithm's effectiveness is demonstrated through a series of analyses comparing it to existing
methods. Our subjective results indicate that our proposed algorithm outperforms the existing methods by 70% in terms of how closely the
output colors match their input counterparts.
 In video processing, achieving high visual quality while keeping file sizes manageable is a
constant challenge. The Constant Rate Factor (CRF) rate control algorithm plays a vital role here, acting as a smart mechanism to
balance quality and compression efficiency. This makes it essential for applications like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing,
where both clarity and bandwidth matter. At
In video processing, achieving high visual quality while keeping file sizes manageable is a
constant challenge. The Constant Rate Factor (CRF) rate control algorithm plays a vital role here, acting as a smart mechanism to
balance quality and compression efficiency. This makes it essential for applications like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing,
where both clarity and bandwidth matter. At  2-pass video rate control is a strategic approach used in latency-tolerant applications, such as Video on Demand (VoD),
where the emphasis is on achieving optimal video quality and precise bitrate management. Unlike single-pass methods, 2-pass
rate control analyzes the video content in two stages, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of both current and future
frame complexities. In this project, implemented in
2-pass video rate control is a strategic approach used in latency-tolerant applications, such as Video on Demand (VoD),
where the emphasis is on achieving optimal video quality and precise bitrate management. Unlike single-pass methods, 2-pass
rate control analyzes the video content in two stages, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of both current and future
frame complexities. In this project, implemented in  In this project, I developed an image segmentation algorithm based in the
In this project, I developed an image segmentation algorithm based in the  The AV1 codec, an open-source video compression standard, excels in intra-frame prediction, where directional
intra modes predict pixel values using neighboring pixels to optimize file sizes. My work at
The AV1 codec, an open-source video compression standard, excels in intra-frame prediction, where directional
intra modes predict pixel values using neighboring pixels to optimize file sizes. My work at  In low-delay applications, such as live streaming and interactive video services, maintaining precise target tracking in rate
control algorithms is essential for delivering consistent video quality and minimizing latency. In this project, I developed an
innovative approach to enhance the target tracking performance of low-delay rate control algorithms. By analyzing the complexity of
different regions within a frame, the algorithm accurately estimates the frame's target size. This detailed analysis allows for more
precise bitrate distribution, resulting in an average improvement of 5% in target tracking performance compared to previous generation
algorithms.
In low-delay applications, such as live streaming and interactive video services, maintaining precise target tracking in rate
control algorithms is essential for delivering consistent video quality and minimizing latency. In this project, I developed an
innovative approach to enhance the target tracking performance of low-delay rate control algorithms. By analyzing the complexity of
different regions within a frame, the algorithm accurately estimates the frame's target size. This detailed analysis allows for more
precise bitrate distribution, resulting in an average improvement of 5% in target tracking performance compared to previous generation
algorithms.
 In the realm of video encoding, optimizing the BD-rate VMAF score is critical for achieving superior video quality while maintaining
efficient bitrate usage.
In the realm of video encoding, optimizing the BD-rate VMAF score is critical for achieving superior video quality while maintaining
efficient bitrate usage.